Find the Right IC — Fast and Confident
Explore verified ICs from TI, ST, NXP, Renesas, onsemi, Microchip, and Melexis. Compare specs, find pin-compatible alternatives, and get a quote within 48 hours.
Technology
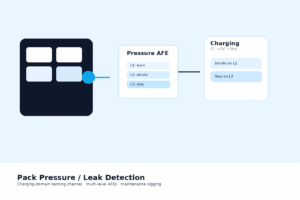
Pack Pressure / Leak Detection (Charging Domain)
← Back to: Battery Charging / Gauging / Protection / BMS Pack Pressure / Leak Detection — Intro & Applicability This page describes low-voltage, pack-internal
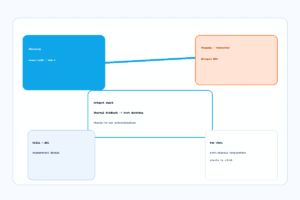
Chassis/Connector Hotspot Guard (Charging Domain)
← Back to: Battery Charging / Gauging / Protection / BMS Chassis/Connector Hotspot Guard in the Charging Branch This page explains a thermal guard that

Pack Pressure / Leak Detection (Charging Domain)
← Back to: Battery Charging / Gauging / Protection / BMS Pack Pressure / Leak Detection — Intro & Applicability This page describes low-voltage, pack-internal

Chassis/Connector Hotspot Guard (Charging Domain)
← Back to: Battery Charging / Gauging / Protection / BMS Chassis/Connector Hotspot Guard in the Charging Branch This page explains a thermal guard that

Pack Pressure / Leak Detection (Charging Domain)
← Back to: Battery Charging / Gauging / Protection / BMS Pack Pressure / Leak Detection — Intro & Applicability This page describes low-voltage, pack-internal

Chassis/Connector Hotspot Guard (Charging Domain)
← Back to: Battery Charging / Gauging / Protection / BMS Chassis/Connector Hotspot Guard in the Charging Branch This page explains a thermal guard that

Pack Pressure / Leak Detection (Charging Domain)
← Back to: Battery Charging / Gauging / Protection / BMS Pack Pressure / Leak Detection — Intro & Applicability This page describes low-voltage, pack-internal

Chassis/Connector Hotspot Guard (Charging Domain)
← Back to: Battery Charging / Gauging / Protection / BMS Chassis/Connector Hotspot Guard in the Charging Branch This page explains a thermal guard that

Pack Pressure / Leak Detection (Charging Domain)
← Back to: Battery Charging / Gauging / Protection / BMS Pack Pressure / Leak Detection — Intro & Applicability This page describes low-voltage, pack-internal

Chassis/Connector Hotspot Guard (Charging Domain)
← Back to: Battery Charging / Gauging / Protection / BMS Chassis/Connector Hotspot Guard in the Charging Branch This page explains a thermal guard that

Pack Pressure / Leak Detection (Charging Domain)
← Back to: Battery Charging / Gauging / Protection / BMS Pack Pressure / Leak Detection — Intro & Applicability This page describes low-voltage, pack-internal

Chassis/Connector Hotspot Guard (Charging Domain)
← Back to: Battery Charging / Gauging / Protection / BMS Chassis/Connector Hotspot Guard in the Charging Branch This page explains a thermal guard that
Application

Pack Pressure / Leak Detection (Charging Domain)
← Back to: Battery Charging / Gauging / Protection / BMS Pack Pressure / Leak Detection — Intro & Applicability This page describes low-voltage, pack-internal

Chassis/Connector Hotspot Guard (Charging Domain)
← Back to: Battery Charging / Gauging / Protection / BMS Chassis/Connector Hotspot Guard in the Charging Branch This page explains a thermal guard that

Pack Pressure / Leak Detection (Charging Domain)
← Back to: Battery Charging / Gauging / Protection / BMS Pack Pressure / Leak Detection — Intro & Applicability This page describes low-voltage, pack-internal

Chassis/Connector Hotspot Guard (Charging Domain)
← Back to: Battery Charging / Gauging / Protection / BMS Chassis/Connector Hotspot Guard in the Charging Branch This page explains a thermal guard that

Pack Pressure / Leak Detection (Charging Domain)
← Back to: Battery Charging / Gauging / Protection / BMS Pack Pressure / Leak Detection — Intro & Applicability This page describes low-voltage, pack-internal

Chassis/Connector Hotspot Guard (Charging Domain)
← Back to: Battery Charging / Gauging / Protection / BMS Chassis/Connector Hotspot Guard in the Charging Branch This page explains a thermal guard that

Pack Pressure / Leak Detection (Charging Domain)
← Back to: Battery Charging / Gauging / Protection / BMS Pack Pressure / Leak Detection — Intro & Applicability This page describes low-voltage, pack-internal

Chassis/Connector Hotspot Guard (Charging Domain)
← Back to: Battery Charging / Gauging / Protection / BMS Chassis/Connector Hotspot Guard in the Charging Branch This page explains a thermal guard that

Pack Pressure / Leak Detection (Charging Domain)
← Back to: Battery Charging / Gauging / Protection / BMS Pack Pressure / Leak Detection — Intro & Applicability This page describes low-voltage, pack-internal

Chassis/Connector Hotspot Guard (Charging Domain)
← Back to: Battery Charging / Gauging / Protection / BMS Chassis/Connector Hotspot Guard in the Charging Branch This page explains a thermal guard that

Pack Pressure / Leak Detection (Charging Domain)
← Back to: Battery Charging / Gauging / Protection / BMS Pack Pressure / Leak Detection — Intro & Applicability This page describes low-voltage, pack-internal

Chassis/Connector Hotspot Guard (Charging Domain)
← Back to: Battery Charging / Gauging / Protection / BMS Chassis/Connector Hotspot Guard in the Charging Branch This page explains a thermal guard that
How It Works
Explore Guides
Read technology & application articles written for real-world use cases.
Compare Approaches
Understand key parameters, pros & cons, and design trade-offs.
Ask an Engineer
Need advice? Share your BOM or questions — we’ll respond within 48 hours.
Need help choosing an IC for your design?
Tell us your requirements — we’ll suggest options and trade-offs within 48 hours.








